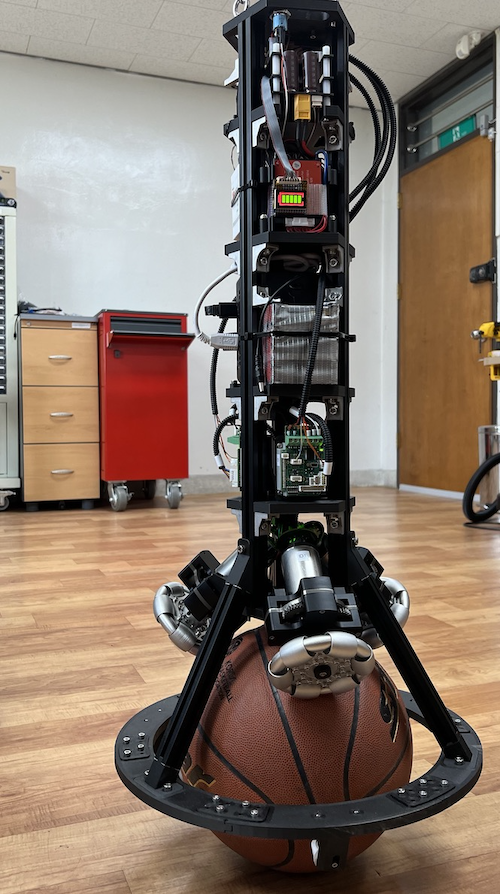
Development of a ball-balancing robot (BBR)
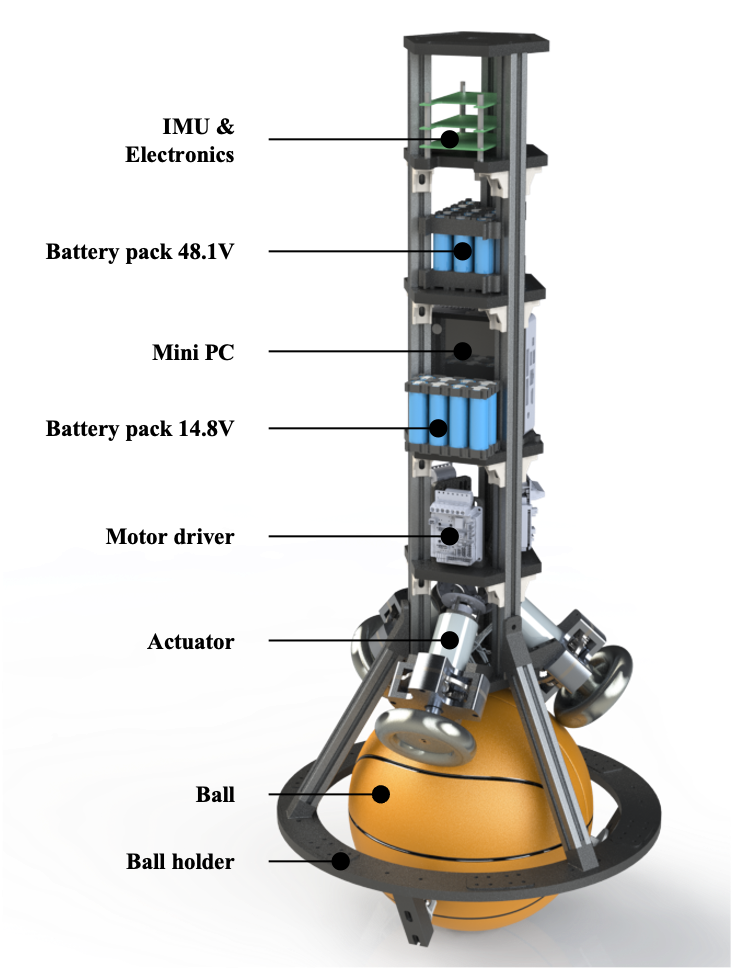
BBR Overview
– Mass: 8.9kg
– Height: 90cm
– Motor: Maxon EC-i 40 100W, 48V BLDC motor x 3
– Speed reducer: a customized stepped planetary gear, ratio 9.04:1
– Motor driver: ELMO G-SOLWHI20/100S x 3
– Communication: CAN 2.0
– Power supply: a 13S1P battery pack(48.1V) for motor drivers and an interface board, a 4S2P battery pack(14.8V) for a NUC PC
– IMU: 6-axis
– PC: NUC13ANKi3, 32GB RAM, 256GB SSD
– Real-time O/S: Ubuntu 20.04 patched with Xenomai
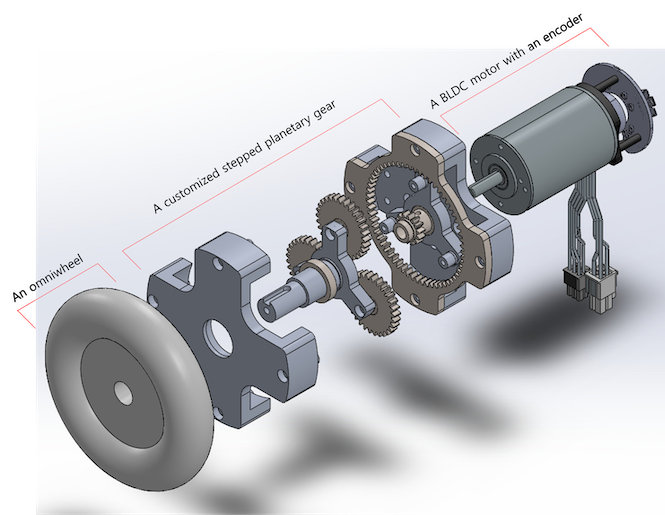
Actuator Design
Each actuator consists of an omniwheel, a customized stepped planetary gear, a brushless DC (BLDC) motor, and a magnetic encoder.
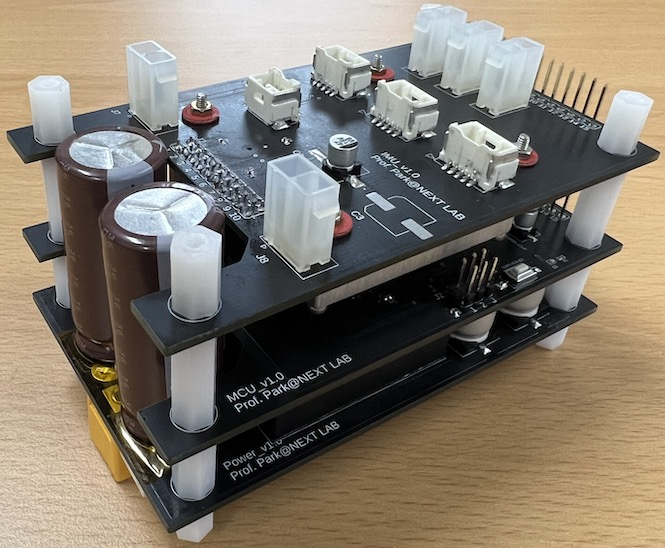
Electrics Design
1. An interface board consists of three PCBs: the first layer is a DC-DC converter PCB, the second layer is a microcontroller PCB, and the third layer is an IMU and connectors PCB.
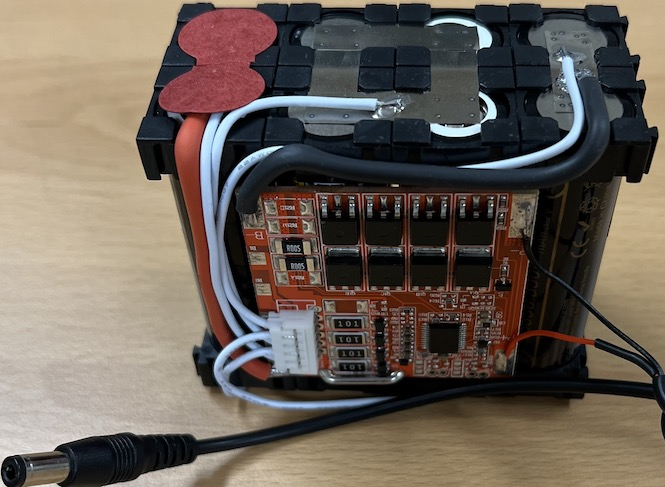
2. The 13S1P battery, used for motor drivers and the interface board, is rated at 48.1V and has a charging voltage of 54.6V.
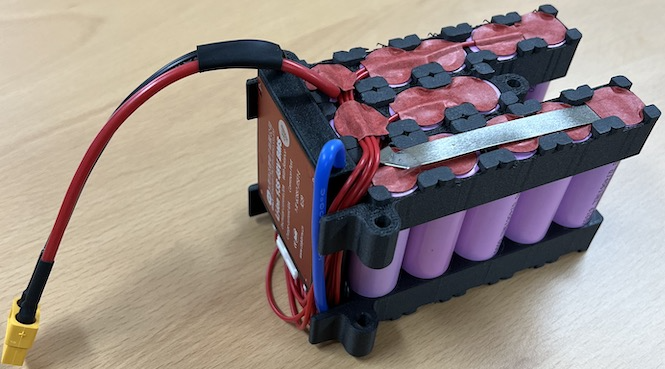
3. The 4S2P battery, used for a NUC PC, is rated at 14.8V and has a charging voltage of 16.8V.
Implement
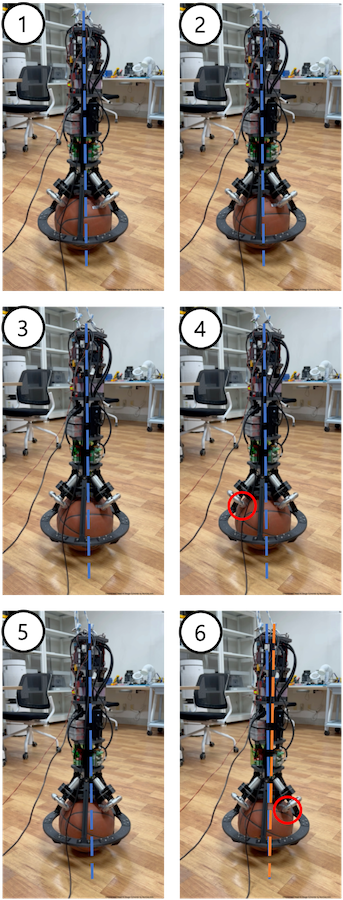
An experiment is conducted to verify whether the developed BBR can maintain an upright position using the applied balancing controller. The balancing experiment is shown, illustrating the robot’s ability to maintain equilibrium.